Manufacturing Processes - Grinding Machines
Grinding Technology - Theory and Applications
Grinding Machines
Grinding machines come in many different forms and types but generally fit under the category of mechanical machining as a manufacturing process.
In principle all grinding machines operate in a similar fashion, they all remove material from a workpiece using tools made from abrasive particles that have an irregular geometry. They work best on hard metals or ceramics. Grinding soft materials is problematic due to the nature of the material which when soft tends to separate from the workpiece in a plastic fashion which can load the grinding tool preventing efficient operation.
A fairly typical structure of a grinding wheel is approximately 45% abrasive particles and 15% vitreous bond. The remainder, 40%, is left as voids in the form of porosity. This porosity is important as a coolant passage and a space in which the metal cuttings can reside temporarily, so this is why the loading of the tool as described in the previous paragraph is a problem, preventing coolant reaching the workpiece and restricting where the removed material can be displaced to.
Grinding operations ignore the optimization of cutting angles and instead depend on the irregular geometry of the abrasive particles to form multiple cutting edges that can remove material when the tool makes contact with the workpiece.This is not particularly efficient and results in high levels of heat energy being produced that has to be cooled.
Grinding processes are typically used for producing components to tight tolerances and with exceptional surface finishes. The size of the abrasive particles and the type of bonding agent used to hold the particles together can dictate the wear rate of the tools and rate of material removal. Contrary to intuitive thought soft wheels with more porosity and low glass content are better for grinding harder materials and for fast material removal. The contrary being true of harder wheels.
Wearing of the individual abrasive particles is of little consequence as long as the wheel overall wears in a reasonably consistent and uniform manner through the contact wear of the bonding, fracture of the particles or loosening of the particles such that they pull out of the bond.
Typical Examples of Grinding Machines
- Surface grinding using a horizontal spindle over a reciprocating table. Workpiece can be held with vacuum or magnetic retaining plates and the use of a coolant is usually employed to keep the workpiece to a reasonable working temperature
- Surface grinding using a horizontal spindle over a rotary table
- Surface grinding using a vertical spindle over a reciprocating table. This is where the flat face of a grinding wheel is used. This process if often used for more rapid material removal
- Surface grinding using a vertical spindle over a rotary table
- Plunge grinding, this is where the grinding stone is formed to be the reciprocal of the required component so when the rotating wheel is plunged into a rotating workpiece the affect is a work piece that is the opposite profile to the wheel, typical use is thread forming.
Pros
- high accuracy and close tolerance components can be produced
- Good surface finishes possible
- Machines tend to be relatively flexible
Cons
- Cooling/lubrication normally required
- Wheels have been know to disintegrate in use, so safety considerations need to be assessed
- Form grinding can be expensive
- Difficult to recycle waste material
Most common grinding wheel abrasives:
- Aluminum oxide
- Silicon carbide
- Diamond
- Cubic boron nitride (CBN)
Other forms of machining that remove materials using abrasives include lapping and honing. Lapping is a surface material removal process that is used typically to meet extremely good surface finish requirements and or close tolerances in microns.
Honing is a figure of 8 reciprocating movement used to remove material from the bore of tubes, the process can be controlled to tight tolerances in terms of internal diameter of the tubes and surface finish, but does not improve straightness tolerances. This is because the stones tend to follow the existing profile of the tube along its length.
Often if tight tolerance straight tubing is required, the only way this can be done is to either select tubing from a standard manufacturing process that meets the specification (can't always be guaranteed) or to use expensive gun drilling operations to produce the bore and then machine the OD to suit while holding on the bore.
Surface Grinding Machine
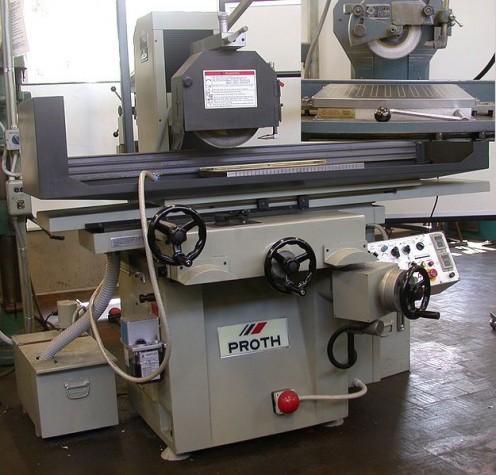

Rotary Grinding Machine - Horizontal Azis
Manufacturing Processes - Mechanical Machining
- Manufacturing Processes and Methods
The selection of a manufacturing process is done very much on the basis of a manufacturer choosing the process that best suits his needs. Consideration must be given to a number of factors before deciding on... - Materials Selection versus Manufacturing Processes
Material selections can determine what manufacturing processes are available, form can determine what materials can be used and manufacturing processes can determine what form can be created. So what you... - Manufacturing Processes - Single Point Cutting
Single point cutting fits in the category of machining as a manufacturing process. It involves the removal of metal from a workpiece using cutting tools that only have one primary cutting edge. Typical...